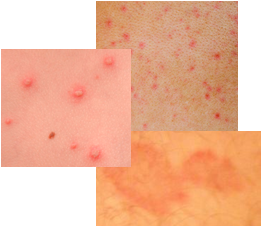
Tinea Versicolor - Skin Fungus Rash
Visit this
PICTURES OF RASHES PAGE
Tinea versicolor is a skin rash problem that is caused by a skin fungus that normally exists on human skin.
Symptoms of this Fungal Rash
The main symptom of tinea versicolor is skin discoloration. This includes the appearance of small and flat light or dark colored patches on the skin. The affected skin areas are oval or round. Spots may join together to give the appearance of one large skin patch. The skin discoloration patches are white, tan, or light brown in color. Occasionally, some pink areas of skin may be present. The actual shade of skin discoloration depends on the base skin pigmentation of the individual. The areas of skin affected by the skin fungus do not result in much discomfort. This is no pain and skin itch is not a standard symptom. Some flakiness of the skin may be present.
The patches of problem skin on affected individuals usually are on the trunk of the body – i.e. the chest, shoulders, back, and upper leg areas. Rarely is the skin on the face affected by the skin fungus. This skin problem is most prominent in the summer months because heat and humidity provide optimum conditions for growth of the skin fungus. It appears that individuals with oily skin are more prone to this skin rash problem as compared with those with dry or normal skin. It is not contagious.
Tinea Versicolor Treatments
Versicolor, like other skin rashes caused by a fungus, is treated with anti-fungal topical creams or lotions. These can be over the counter type or prescribed by a physician. Sometimes oral medications to combat the skin fungus are required. There is a good probability that tinea versicolor will recur and therefore, additional treatments will be required after the initial round of medication.
Other treatments for the fungal skin rash involve the use of a dandruff shampoo containing selenium sulfide. Selenium sulfide will kill the fungus when used as directed. The shampoo is applied onto the skin areas that contain the fungus. It is left on the skin overnight and rinsed off in the morning. This procedure is repeated every night for a week. Note that selenium sulfide may cause additional skin irritations. Consult a physician first before trying.
Restoration of normal skin color will occur on its own, but several months will be required to eliminate the skin discoloration. This is true for the lighter skin patches. Darker patches of skin discoloration tend to fade much quicker. In most cases, the skin will indeed go back to its normal skin pigmentation after proper treatment of the tinea. Sun tanning will make the skin discoloration more obvious and therefore should be avoided.
Other skin problems often confused with this skin problem include: pityriasis alba, vitiligo, and pityriasis rosea.
Other fungal type skin rashes:
ringworm | tinea pedis | more rash types