- Home
- Eczema
Eczema Types, Causes, and Treatments
Visit this
PICTURES OF RASHES PAGE
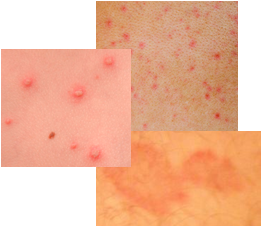
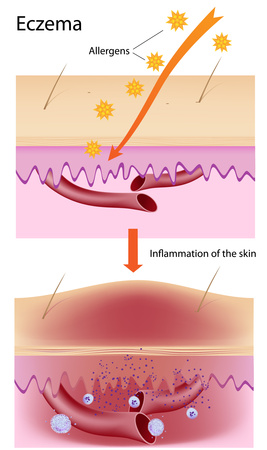
Eczema is also known as dermatitis. It is a term used to describe a group of dry skin conditions that can affect any age group. This skin problem is not contagious and although there are treatments, there is no cure. Generally, it is characterized by itchy red skin with tiny bumps or blisters and inflammation. Over time the untreated condition will lead to skin that is thick, scaly and dry. There may also be hair loss in the affected areas and changes in the colour of the skin. Severe cases include large areas of the body being affected and the presence of significant open areas and oozing fluid.
Visit the pictures of eczema page for more information on eczema.
If you have an eczema story that you would like to share with other eczema sufferers, this visit this page.
Eczema Causes and Types
An individual may experience several different types of excema. The causes and treatments will vary depending of which type the individual is suffering from.
Atopic
- can affect all age groups, although generally starts at a young age (around 20% of children younger than 6 months have this skin problem
- most common type and affects about 10% to 20% of the population
- it is hereditary or in other words, children whose parents have atopic eczema are more likely to develop it themselves
- closely associated with other health problems such as asthma, allergic rhinitis and hay fever
- it is suspected that individuals with atopic eczema are more sensitive to allergens such as dust, dust mites, pet dander, pollen, molds, and certain foods
- other triggers can be stress, sweating, or exposure to hot or cold temperatures
- common symptoms are severe itchiness (pruritis), dry and cracking skin, sore sensitive skin, red to brownish-grey blistery skin, and inflammation
- symptoms usually come and go
- skin may also become thick and leathery
- all areas of the body can be affected, especially skin folds, the back of knees and elbows, neck, wrists, ankles, and face
- infection commonly occurs as a result of scratching opening up the skin surface
- in about half of the infant cases, the condition disappears by a year and half in age
- usual treatments include emollients in order to hydrate the skin and steroids to reduce inflammation
- to reduce the effect of dust mites triggering the eczema, plastic mattress pads should be used on the bed, regular vacuuming of curtains and rugs and damp dusting is necessary
- altering the diet may be necessary when the trigger is an allergy to food
For more information on treatments, please visit the cure page.
Irritant Contact Dermatitis and Allergen Contact Dermatitis
For information on these conditions, please visit the dermatitis page.
Infantile Seborrhoeic
- commonly affects infants less than 1 years old
- also know as “cradle cap”
- exact cause of this skin condition is unknown
- usually starts at the scalp or diaper area as greasy yellow scales or rash and then spreads
- looks uncomfortable, but there is minimal itch and skin soreness
- will normally clear on its own within a few months
- moisturizing creams may help speed recovery
- areas may become infected with bacteria or fungi
- antibiotic or antifungal cream may be necessary for treatment
Adult Seborrhoeic
- affects adults (usually males) between the ages of 20 to 40
- a yeast growth is a suspect cause for this skin problem
- usual symptom is a mild case of dandruff
- can spread to facial and chest areas
- skin is red, flakes, and is inflamed
- in adults, unlike children the condition can continue for several years
- infected skin caused by this type of excema is often treated with an anti-fungal cream
Varicose (or Gravitational or Stasis)
- adults in the middle to late years are vulnerable
- caused by poor circulation and associated with varicose veins
- affects the lower legs, especially around the ankles
- skin is speckled, itchy, inflamed and may have sores
- emollients and steroid creams are common treatments
CAUTION: If left untreated, eventually a skin ulcer can develop.
Discoid (or Nummular)
- a condition that affects adults and is most common in middle-aged men
- small areas of scaly red skin develop (coin shaped) that are very itchy and can leak fluid
- arms, trunk and lower legs are the usual body areas affected
- usual treatment is with emollients/moisturizers (and perhaps steroid creams)
Light Sensitive
- a rare condition triggered by sunlight
- can be caused when taking certain antibiotics, antihistamines, or arthritis drugs
- ingredients in soaps and cosmetics may also be a trigger
- target areas of the body are the face, hands and arms
- high SPF sun creams can prevent and treat this problem
Juvenile Plantar Dermatosis
- more common in males during puberty
- caused by modern athletic footwear that does not fit properly, creating a sliding friction on the sole of the foot
- sole of foot becomes hot, red, sore and with a glazed look
- using leather footwear and wearing cotton socks will prevent this from occurring and allow the skin to recover
- emollients or ointments may be part of the treatment
Dishydrotic (Pompholyx)
- cause is generally unknown, but may be related to allergic contact dermatitis caused by nickel containing compounds
- this condition is aggravated by stress
- characterized by very itchy vesicles on the hands and soles of feet
- itching can be relieved by oral antihistamines
- calamine lotion can be used to soothe the skin
Asteatotic
- prevalent in older adults with thin and dry skin
- large dry scales appear on the skin surface and usually starts on the lower leg region
- skin may also be dry and red
- may be caused by soap remaining on the skin (as a result of a sponge bath)
- proper removal or less use of soap can prevent or alleviate the problem
- moisturizer can help as well with treatment
- avoid the use of steroid creams because the aged skin is more fragile
Lichen Simplex
- caused by repeated scratching or rubbing the same skin area, leading to patches of very thick and tough skin
- a very itchy condition
- usually found on legs, wrist, ankle, groin, and back of the neck
For an all natural treatment for this skin problem visit the natural cure page.