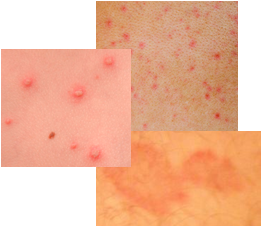
Syphilis Rash
Visit this
PICTURES OF RASHES PAGE
A syphilis rash is a common symptom of a person infected with syphilis. Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease that is caused by a bacterium known as Treponema Pallidum. If left untreated, the disease can eventually lead to cardiovascular disease, neurological disorders, blindness, and eventually death.
Syphilis is passed on to healthy individuals when these individuals come in direct contact with syphilis ulcers. Usually this occurs during sexual contact in the genital, anal, lip, or mouth regions. It can also be spread through blood transfusions. The syphilis bacteria cannot be spread by sharing clothing or eating utensils or by coming in contact with doorknobs or toilet seats.
The syphilis disease progresses in stages. There are four stages and a syphilis rash is a front and center symptom of syphilis. It takes anywhere from one week to three months before an infected person begins to show symptoms of the first stage. The average is three weeks. A person is contagious during the first two stages of the syphilis disease.
Primary Syphilis
The first stage is known as the primary stage or primary syphilis. Initially, the main symptom is not a widespread syphilis rash, but rather a single red firm and round bump that is rather painless. After a while the bump ulcerates and is known as a chancre. In some cases, there may be more than one chancre. Because for the most part it is painless and is likely to reside inside the genitals, it often goes unnoticed. However, the sore can be on the lip, tongue, or mouth area as well. The chancre appears at the site that the syphilis bacteria entered the body. The sore usually takes one to two months to heal and heals without any treatment. However, treatment is necessary to prevent the disease from progressing to the next stage.
Secondary Syphilis Rash
The secondary stage occurs three to twelve weeks after the initial sore appears if no treatment has been administered. The main symptom is a widespread rash. The rash can be described as rough and red or as reddish brown spots. This rash can be anywhere on the body, but often is found on the palms of the hands or bottom of the feet. The rash from syphilis is often not very itchy and can be quite faint and hard to notice. Other symptoms include hair loss in patches, red and irritated mucous membranes (mouth, throat, genital areas, anus), fever, tiredness, swollen lymph nodes, muscle aches, weight loss, and headaches. Generally the symptoms of the secondary stage or secondary syphilis are similar to the flu. The rash also appears as greyish-white moist raised patches in the groin, inner thigh, armpits, or under the breasts. The rash caused by syphilis disappears without treatment, but lack of treatment causes the disease to progress to the next stage.
Dormant or Latent Syphilis
The third stage is the latent or dormant stage. This stage begins once the secondary stage has passed and may last for many years. During this stage, the secondary symptoms may periodically occur and a rash may develop. If no treatment occurs during this stage, then the syphilis progresses to the final stage.
Final or Late Stage Syphilis
During the final stage major health problems develop such as damage to nerves, the brain, eyes (leading to blindness), heart, blood vessels, liver, bones, and joints. Eventually paralysis and death will result from the complications of the disease.
It is best to pursue treatment early before a syphilis rash turns into something much more serious. Penicillin injections can be used to treat the syphilis and prevent the disease from progressing.
Other skin rashes caused by bacteria:
strep | syphilis rash | lyme disease | impetigo | cellulitis | other skin rashes