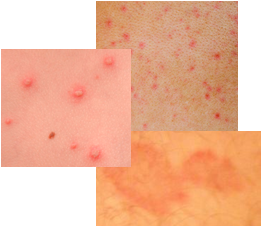
Staph Infection Symptoms
Visit this
PICTURES OF RASHES PAGE
Basic Symptoms
What are the staph infection symptoms? There are some basic symptoms of a staph infection to be aware of. The area being affected by a staff infection may show redness, inflammation of the skin, skin warmth, pain or tenderness, drainage of fluid or pus with crusting, and presence of boils or abscesses.
Usually these basic symptoms of a staph infection begin as only a very small skin area being affected and the symptoms can be often mistaken for pimples or insect bites. Often a small cut or skin break is in the center of these symptoms, but sometimes there is no clear skin break evident. The break in the skin may be as small as a pinhole.
Advanced Staph Infection Symptoms
If the staph infection symptoms do not subside on their own, then the next stage of symptoms will become evident. For example, the affected individual will likely develop a fever as the infection becomes more intense and begins to spread. The individual will also likely exhibit the typical signs of fever such as chills and sweating. The staph symptoms described above become more intense – more swelling, more redness, more pain, and more pus evident.
If the infection progresses even more then it will not be confined solely to the skin but will enter the bloodstream and cause other health problems with the heart, lungs and other organs.
Other Infections Caused by the Staph Bacteria
More specific staph symptoms are associated with various other infections caused by the staph bacteria.
For example, cellulitis symptoms are redness, swelling, skin warmth, and pain, but often with no pus or drainage. Spreading leads to a general ill feeling and fever. This is a deep tissue skin infection and the legs are usually affected.
On the other hand, impetigo is more of a surface skin infection. Symptoms typically target the areas of the face, hands, and feet and are characterized by the presence of a honey colored crust on the affected areas. The crust may itch and ooze. Fever and pain are not normally present.
Folliculitis is the infection of the hair follicles. The staph symptoms for folliculitis include the presence of pimples with white heads at the base of the hair shaft.
A sty is a staph infection of the eyelid. The symptoms are a painful, red, and swollen area on the eyelid.
Diagnosing a Staph Infection
Diagnosis of a staph infection can generally be performed by noting whether the staph infection symptoms are present. However, because this can be a serious skin and health problem, the diagnosis should be performed by a physician who is more experienced at examining the infection problem and more capable to properly assess the infection symptoms. Is the problem a serious infection or is it minor problem that can be easily treated? A physician will be able to perform a proper diagnosis.
As stated above, the basic symptoms of a MRSA infection are redness of the skin, inflammation or swelling of the skin, oozing of pus from the wound or damaged skin area, and in more advanced cases significant pain in and around the problem skin area. A fever is also a common symptom and is a key indication that the infection is not minor and is progressing towards a more serious state. Knowing if a person has had a similar infection in the past also contributes valuable information to the diagnosis process.
Determining, with one hundred percent certainty, if the infection is MRSA or in other words whether the infection is resistant to certain antibiotics or is simply a minor infection, requires in depth laboratory testing. This testing requires the sampling of blood and also acquiring fluid or pus samples that are taken directly from the infected area. These samples are then cultured or in other words placed under favourable conditions for the bacterium to grow so that it can be properly identified. From these samples, a proper skin infection diagnosis can be made so that either standard antibiotics are prescribed by the physician or more powerful antibiotics are prescribed if the infection was determined as being a MRSA infection.
Culture tests can take up to two days for results and this can be problematic where results are required faster. New tests that look at DNA are becoming more popular and will allow for the faster diagnosis of a staph infection and consequently and more successful treatment.
Other staph infection symptoms related resources:
staph | cellulitis | diagnosis | causes | treatments