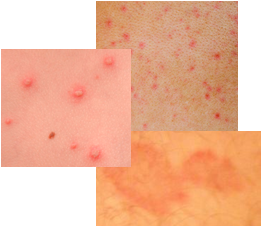
Impetigo Treatment
Visit this
PICTURES OF RASHES PAGE
Impetigo treatment options are very important because this skin infection is very contagious. If the sores in the affected area are scratched or touched, the condition can spread to other parts of the body and even to other people. The infection can also be spread by coming in contact with clothing, towels, bedding, and other objects that have been in contact with a person with impetigo.
Impetigo Treatment Options
Prevention of Impetigo
As with many other skin conditions, prevention can be an effective impetigo treatment. Good hygiene such as regular hand washing, use of antibacterial soap and water to clean the skin, and regular bathing can be useful in preventing this skin problem.
Any injured skin areas as mentioned previously should be properly looked after by treating them as required. These areas need to be kept clean and covered to keep dirt and bacteria out of the wounded skin area in order to prevent infections from developing.
To prevent the spread of impetigo, the infected skin is usually covered loosely with clean gauze and held in place with medical tape. Keeping fingernails short also helps prevent the spreading of this infection to other body parts. Infected individuals should only use their own towels and they should not be shared. Keep the clothing, bed linens, and towels of the infected individual separate from others and wash separately in hot water. Children should be kept away from school or daycare until the condition is under control to prevent the spread of this skin condition.
Depending on the extent of the problem, there are various impetigo treatment options.
Leaving the Affected Area Alone
The first impetigo remedy option, if the area affected is very small, may be to simply leave it alone. Minor infections may clear on their own in a couple of weeks. However, it is prudent to pursue a more aggressive treatment for impetigo in order to prevent a more serious infection and other complications from occurring such as:
Poststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis
- also known as PSGN
- is an inflammation of the kidney that occurs after a streptococcal type infection
- caused by dead bacteria and antibodies becoming trapped in the small tubes that filter waste in the kidneys
- can eventually lead to kidney failure
- usually occurs about two weeks after infection
- symptoms include facial swelling, decreased urination, blood in the urine, stiff and painful joints, and a increase in blood pressure
Meningitis
- a serious infection and inflammation of the membranes and fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord
- symptoms are a high fever, severe headache, and vomiting
- can lead to hearing loss, blindness, brain damage, behaviour problems, and death in a small percentage of cases
Cellulitis
- this infection affects the tissues underneath the skin
- the infection may spread to the lymph nodes and blood
- this is a life-threatening condition if untreated
Antibiotic Ointment Impetigo Treatment
For small areas of the skin, an antibiotic ointment such as fucidic acid or mupirocin can be a very effective impetigo remedy. These ointments are usually applied three times per day and continued for several days after healing.
Oral Antibiotic Treatment
In cases where the infection is widespread or is more severe, then oral antibiotic impetigo treatments are prescribed. The treatment for impetigo may also be necessary when ointments are ineffective. Flucloxacillin over a seven-day period is often prescribed to combat this problem.
With either oral or ointment antibiotic treatments, the skin condition should begin to show improvement within a few days. As always, the antibiotic should be used as prescribed. The treatment should not be stopped early unless directed by the physician. After antibiotic treatment for 24 to 48 hours, an individual with impetigo is no longer contagious. Without treatment, a person can be contagious for several weeks.
Other Impetigo Skin Infection Remedy Tips
When impetigo begins to heal, it is important to keep the infected area clean. This can be accomplished by gently washing the infected skin daily with a clean gauze and antiseptic soap. The crusted skin can be removed by using warm soapy water. This is important to perform since it will allow antibiotic ointments to have access to the bacteria underneath the crusted skin. Proper hygienic measures can be an effective impetigo treatment for minor cases of the disease.
If a fever develops with impetigo, it is best to consult with a doctor immediately. The same holds true if the area around the infected area becomes red, warm, and very tender to the touch. These could be signs that the treatment for impetigo is not working and the condition is getting worse and more serious complications are developing.
Impetigo resources:
symptoms and types | impetigo treatment