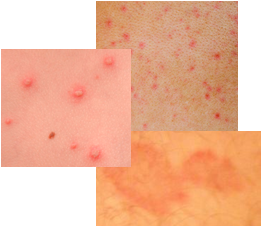
Follicular Keratosis
Visit this
PICTURES OF RASHES PAGE
Follicular keratosis is another type of keratosis skin problem. It can be referred to by many other names. Examples of such names are keratosis follicularis, darier disease, dariers disease, or darier’s disease, to name a few.
This type of keratosis originates from the hair follicle in the skin. It commonly affects the hands, face (ears, sides of the nose, forehead), scalp, neck, chest, back, thighs, groin, and abdomen. It is hereditary and this genetic disorder is considered rare.
Darier disease is not contagious, can affect both sexes, and usually begins to be present in the late adolescent years. Sunlight, as well as heat and humidity, irritate this keratosis follicularis skin problem.
Symptoms of this Skin Problem
The symptoms of the affected skin areas include the appearance of dark crusty skin patches that are brown, yellow-brown, or may be skin colored. There is itching of the affected areas. The growths may be greasy and scaly warty type or be similar to papules that may fuse together and look like one large growth. Pus is not always present but may appear in the skin patches.
An interesting symptom of follicular keratosis is that the rash usually emits a distinct odor. Finally, many darier disease suffers will have broad red and white stripes on the nails of their hands.
Follicular Keratosis Treatments
There are various treatments that can be pursued for this skin care problem. Moderate type treatments involve the use of moisturizers and sunscreen to avoid irritating this type of skin rash when outdoors. Keeping the skin cool and dry by wearing light clothing, for example, helps as well.
Treatments that are more extensive involve the use of oral or topical retinoids or antibiotics to treat bacterial infections that may flare up. Topical corticosteroids may also be used. Other more extensive treatments for keratosis follicularis can include dermabrasion to smooth out the growths, electrosurgery, and laser treatments.
More information on different types of keratosis:
keratosis | actinic | actinic cheilitis | follicular keratosis | pilaris | seborrheic | senile