Symptoms of Bed Bug Bites
Visit this
PICTURES OF RASHES PAGE
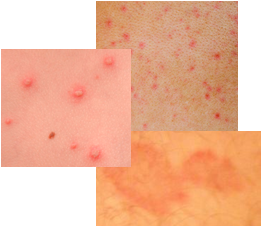
Bed Bug Rash Symptom
Symptoms of bed bug bites are often in the form of a rash that can occur when you have been bitten by bed bugs.
The rash caused by the bites appears like a number of small hives. These hives tend to be in a cluster or orderly row pattern. The hives do itch like mosquito bites and in fact, like mosquitoes, bed bugs inject their saliva into the skin of the individual prior to biting.
The saliva contains an anesthetic to keep the person from feeling the bite (so that the person stays asleep) and an anticoagulant in order to keep the blood from clotting so that it can be easily extracted from the human. The hives and redness and other symptoms are usually the body’s reaction to the saliva. Over the course of a few days after the biting has occurred, the hives will subside; leaving red marks that do not itch. These marks will eventually fade as well.
Sometimes the body reacts more aggressively towards
the bed bug bites and there are other symptoms of bed bug bites that become evident. If the body is allergic to the bites then the rash may be a
general body rash. This may or may not be accompanied by more severe symptoms
such as difficulty breathing and swollen lips or tongue. The allergic reaction
to the bites may also be more localized. In this case the hives tend to be much
larger and spread out more from the bite site than the typical bed bug skin
rash. In addition, large puss-filled blisters often appear in the affected
area.
If you are unfortunate enough to have been exposed and bitten by bed bugs, you can usually find the bedbug skin rash on the upper body, face, neck, and arms. However, bed bugs are not all that finicky and will bite any available area if they need to feed.
The resource diagnose my rash provides more detailed information on bug bites and skin rashes.
Other Symptoms of Bed Bug Bites
A bed bug bite is becoming a fairly common occurrence in homes and hotel rooms.
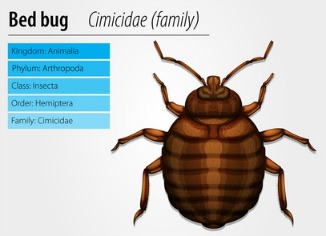
Bedbugs are flat oval shaped reddish-brown insects that are about 5 mm in length at full maturity and look like ticks. Bed bugs survive by feeding on the blood of humans or any mammal. After they feed, the bodies become rounder. When they bite, bed bugs inject their saliva into the skin. Like mosquitoes, this saliva contains an anticoagulant to keep the blood flowing freely as the insect sucks and an anesthetic agent to keep the victim from feeling the bite. Consensus is that bedbugs do not spread any diseases to humans like mosquitoes are known to do.
Typical symptoms of bed bug bites are the presence of small hives usually in an orderly row or clustered pattern. Skin redness and itching are also very likely and are a reaction to the bed bug’s saliva. Over time the hives are reduced to only red marks on the skin and these generally disappear over a period of a few days. Bed bugs are active and bite at night, and will bite all over a human body, especially around the face, neck, upper torso, arms and hands.
Any exposed skin during sleep is a target area. During the day bed bugs will hide in a variety of dark and isolated places. Favorite hiding sites include the bed frame, mattress and box spring, cracks, and behind loose paint or wallpaper.
Because of the itchiness of the bite, scratching is a problem. Too much scratching will lead to open skin with infection becoming a possibility.
Treatment of a this kind of bed bug bite is similar to a mosquito bite. However, in cases where allergic symptoms occur, then medical treatment is required. Allergic symptoms include: much larger hives that can be up to 20 cm in diameter and the development of large puss-filled blisters. In rare cases, anaphylactic shock may occur.
The symptoms of bed bug bites are often mistaken as those from flea or mosquito bites. However, bed bugs emit a certain odor (an intense, sweet odor) and leave dark fecal spots on bed sheets or mattresses. If these signs are noticed, then the marks on your skin when you wake up are likely due to a bedbug bite.
Additional bed bug bite information can be found below:
symptoms of bed bug bites | pictures